while select in X++ is one of the most common constructs you’ll encounter in AX / D365FO development. It’s used to fetch records from the database and loop through them one by one, letting you perform actions on each record inside the loop.
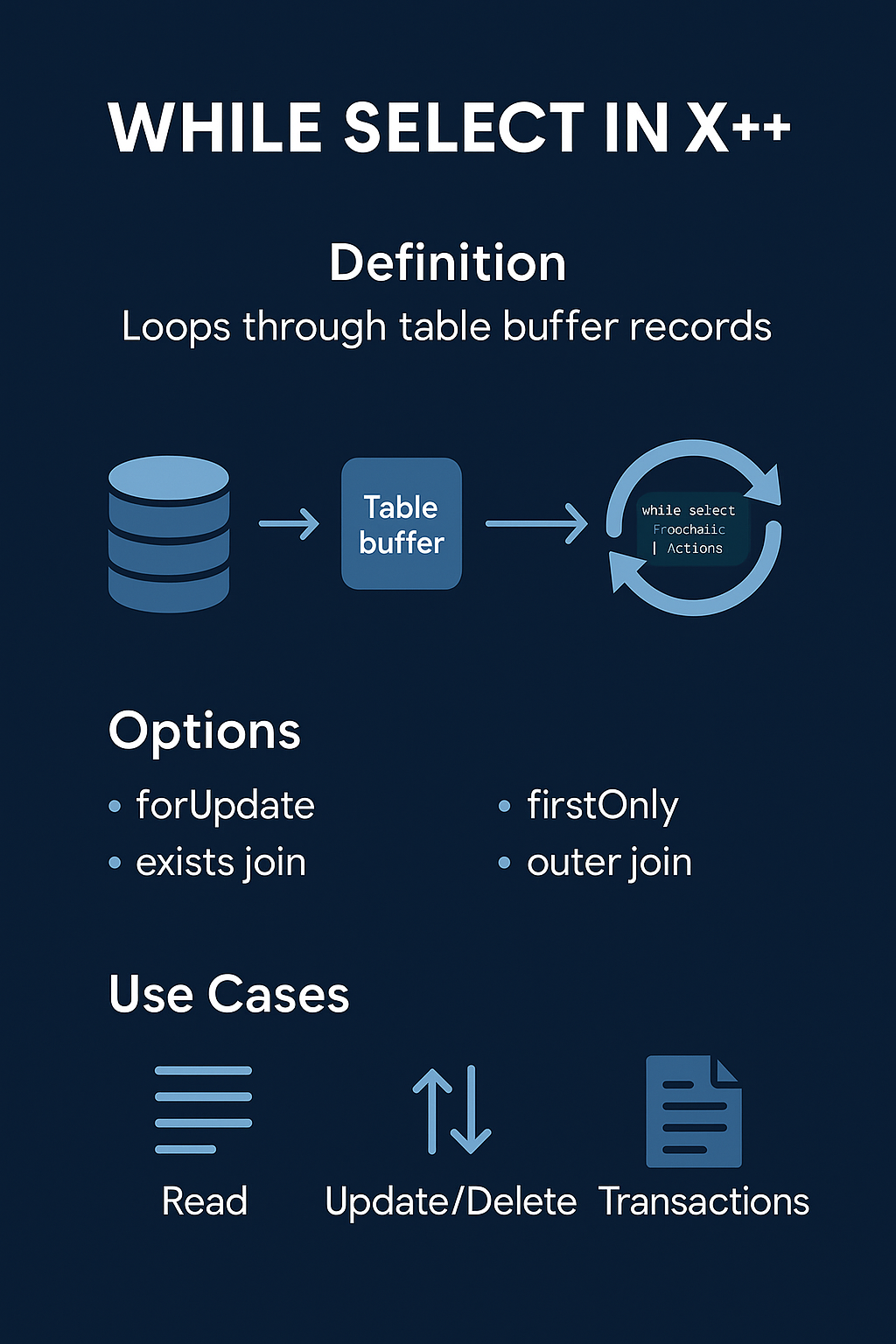
You can think of it as a combination of a SQL cursor and a loop, but for while select X++ means it’s much simpler and tightly integrated with the table buffers.
Here’s the general form:
while select Field1, Field2 from CustTable
where CustTable.Blocked == CustVendorBlocked::No
{
info(strFmt("Customer: %1 - %2", CustTable.AccountNum, CustTable.Name));
}
In this example, the select retrieves all non-blocked customers from CustTable. The while keyword means the code runs through each record one at a time, and the buffer (CustTable) is populated with each row in turn. Inside the loop, you can access the fields, call methods, or even update or delete the record.
How it works under the hood
When you learn about your select statements in x++ language you learn how to write a while select, and know that the system translates it into a SQL query against the database. The runtime fetches rows, fills the table buffer, and advances the loop until there are no more rows. By default, it locks as little as possible—just enough to read data.
You can change behavior in how to write a while select statement with keywords:
forUpdatetells the system you intend to modify the records, so it locks them.firstOnlyfetches only the first record.exists joinorouter joincan be used to join multiple tables.
For example, a loop where you plan to modify:
ttsBegin;
SalesLine line;
while select forUpdate line
where line.SalesStatus == SalesStatus::Backorder
{
line.SalesStatus = SalesStatus::Canceled;
line.update();
}
ttsCommit;
Here, the forUpdate signals that records are being changed, and the update() persists the modifications inside a transaction.
Why use x++ while select statement in the d365fo programming language?
- It’s intuitive: you work directly with table buffers as objects.
- It gives fine-grained control: you can validate, calculate, or branch per record.
- It integrates with transactions: combined with
ttsBegin/ttsCommit, it supports safe updates.
But performance matters: for bulk operations (e.g., deleting or updating thousands of rows), while select can be slower than set-based alternatives like delete_from, update_recordset, or insert_recordset. Still, when custom business logic per record is required, while select is the right tool.
Have a Question ?
Fill out this short form, one of our Experts will contact you soon.
Talk to an Expert Today
Call Now